The paleo diet is a popular eating pattern that has gained a lot of attention in recent years. Based on the principle of eating like our ancestors, this diet has many potential benefits, but also some drawbacks that are important to consider. In this article, we will explore what the Paleo Diet is, how it works, and what the science says about its benefits and drawbacks.

What is the Paleo Diet (PD)?
This diet is a way of eating that mimics the diets of our ancestors from the Paleolithic era. Our ancestors ate a diet primarily made up of vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, and meat. The PD eliminates modern foods that are believed to be harmful, such as processed foods, dairy products, grains, and legumes.
Composition
It’s composed of whole, unprocessed foods that were available to our ancestors during the Paleolithic era. These foods include:
- Meats: grass-fed beef, poultry, pork, lamb, and game meats are included in the PD.
- Fish and seafood: fatty fish like salmon and sardines are recommended, as well as shellfish.
- Vegetables: all types of vegetables, especially leafy greens, are encouraged on the PD.
- Fruits: all types of fruits, particularly berries, are allowed on the PD.
- Nuts and seeds: almonds, walnuts, cashews, sunflower seeds, and pumpkin seeds are all part of the PD.
- Healthy fats: olive oil, coconut oil, avocado, and organic butter are encouraged on the PD.
The PD restrict processed foods, refined sugars, artificial sweeteners, and grains, as these were not available during the Paleolithic era. The focus is on eating whole, nutrient-dense foods to support optimal health and wellness.
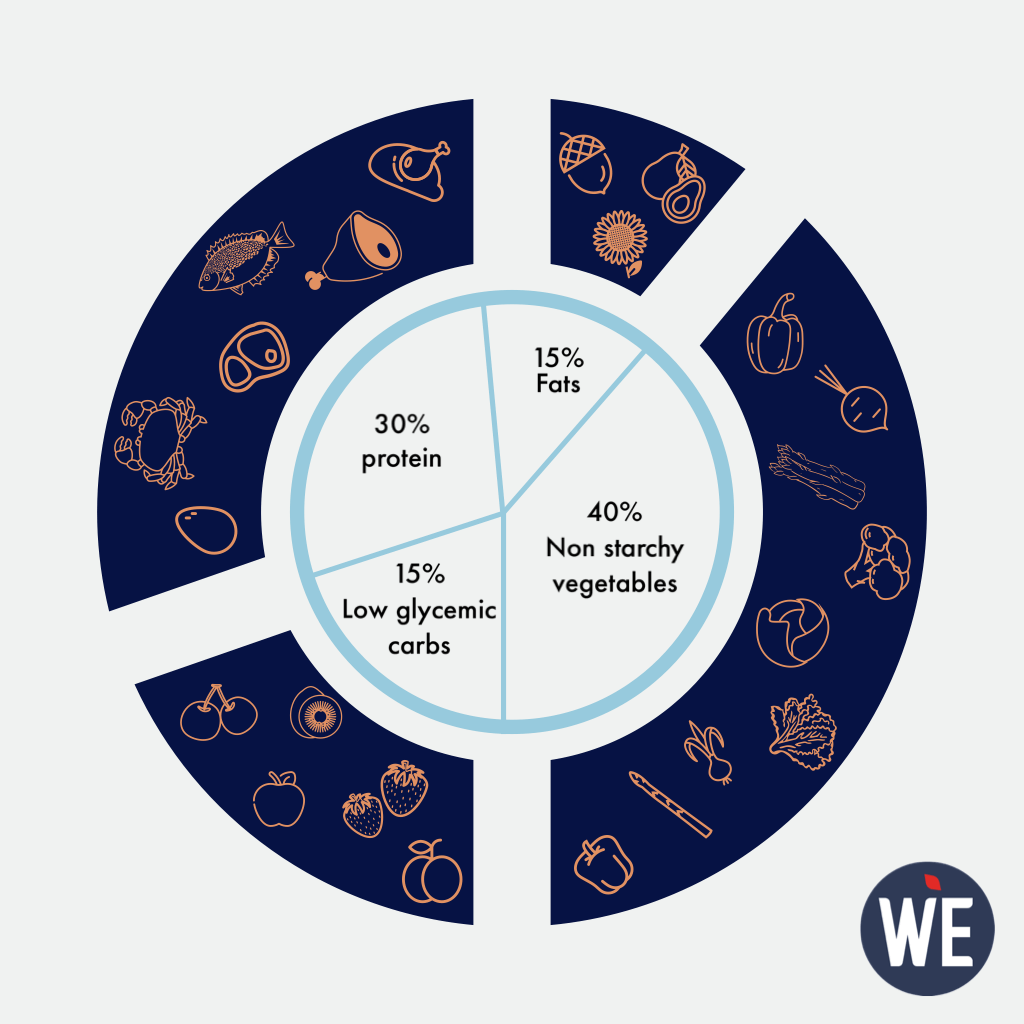
Macronutrients Requirements
There are no specific percentage guidelines for macronutrient intake on the PD. Instead, the focus is on eating whole, unprocessed foods in appropriate portions. However, many people on PD consume the following macronutrient ratios:
- Fat: Approximately 30-40% of daily caloric intake comes from healthy fats such as olive oil, coconut oil, avocados, and nuts.
- Carbohydrates: Approximately 30-40% of daily caloric intake comes from carbohydrates, mainly from fruits and vegetables.
- Protein: Approximately 20-30% of daily caloric intake comes from protein sources such as grass-fed beef, poultry, pork, lamb, fish, and eggs.
Principles
The thumb rules of the paleo diet is based on the following principles:
- Eating whole, unprocessed foods
- Eliminating processed foods, grains, legumes, and dairy products
- Emphasizing vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, and meat
- Limiting or eliminating added sugars, artificial sweeteners, and vegetable oils

Benefits Of The Paleo Diet
There are several potential benefits of a paleo diet, includes the foloowing:
- Weight loss: The PD is naturally lower in calories and carbohydrates, which can lead to weight loss.
- Improved heart health: The PD emphasizes healthy fats, which can help improve heart health.
- Increased energy: By avoiding processed foods and added sugars, many people report increased energy levels on the PD.
- Better digestion: By eliminating grains and legumes, which can be difficult for some people to digest, the PD can improve digestion for some individuals.
Drawbacks
While the PD has many potential benefits, there are also some drawbacks to consider:
- Difficulty following the diet: Eliminating many food groups can make the PD difficult to follow for some people.
- Potential nutrient deficiencies: By eliminating certain food groups, there is a risk of nutrient deficiencies, such as calcium and vitamin D.
- Cost: Eating a diet primarily made up of meat, fruits, and vegetables can be more expensive than a typical Western diet.

Paleo Diet And It’s Relation To Weight Loss
The paleo diet leads to weight loss in several ways:
- Elimination of processed foods: The PDeliminates processed foods and focuses on whole, unprocessed foods, which are often lower in calories and higher in fiber. This can help reduce calorie intake and promote feelings of fullness, leading to weight loss.
- Increased consumption of fiber-rich foods: The PD emphasizes the consumption of fiber-rich fruits and vegetables, which can help support weight loss by promoting feelings of fullness and reducing calorie intake.
- Focus on high-protein foods: The PD places a strong emphasis on high-protein foods such as meats, poultry, fish, and eggs, which can help support weight loss by promoting feelings of fullness and reducing calorie intake.
- Limitation of added sugars and artificial sweeteners: The PD limits added sugars and artificial sweeteners, which can contribute to weight gain. By reducing the intake of these calorie-dense, nutrient-poor foods, the paleo diet can support weight loss.
It’s important to note that weight loss results may vary based on individual factors such as age, gender, activity level, and starting weight. It is recommended to speak with a healthcare provider before starting any new diet, especially for weight loss purposes.
Conclusion
The paleo diet is a popular eating pattern with many potential benefits, but also some drawbacks to consider. Before starting the PD, it is important to talk to a healthcare professional to determine if it is the right choice for you. If you do decide to follow the paleo diet, it is important to make sure you are getting all the necessary nutrients and to monitor your health closely.